| KyteLabs InfoBase - Semiconductor Data |
Last modified: 2016-11-19 (18644) |
| B |
Solid-State Technology History and Basics |
| B.8 |
Glossary - Explanation of Semiconductor and Electronics Terminology |
[DE] |
Absolute Maximum Ratings - must not be exceeded under no circumstances.
Power supply voltage variations, component tolerances, etc. should be carefully taken into account.
Exceeding only one of these maximum ratings can seriously damage the device.
Emitter-to-Base Floating Potential - UEB(FL) is the DC open-circuit voltage between the emitter terminal and the base terminal when the collector terminal is biased in the reverse direction with respect to the base terminal.
FREDFET - Fast-Recovery Epitaxial-Diode Field-Effect Transistor 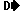 - is a field-effect transistor with with fast-switching inverse diode.
- is a field-effect transistor with with fast-switching inverse diode.
Punch-Through Voltage - UCB(PT) is determined by measuring the emitter-base floating potential UEB(FL), using a voltmeter with 11 megohms minimum input impedance.
The collector-base voltage, UCB, is increased until UEB(FL) = –1.0 Vdc; this value of UCB = UCB(PT)+1.
Second-Breakdown Collector Current - IC (SB) is defined as the current at which second breakdown occurs at a specific collector voltage with the emitter-base junction forward biased for transistor operation in the active region.
Second-Breakdown Energy - E (SB)X is defined as the energy at which second breakdown occurs under specified reverse-biased conditions.
E (SB)X = ½LI², where L is a series load or leakage inductance and I is the peak collector current.
![]() - is a field-effect transistor with with fast-switching inverse diode.
- is a field-effect transistor with with fast-switching inverse diode.